Occupancy Grid based Model Predictive Control
Mathematically
modeling the surrounding environment is an essential part of motion planning
for autonomous driving. However, this process becomes very difficult as the environment
becomes more irregular and complex. In this regard, “Occupancy Grid” has several advantages. An
occupancy grid is a representation of the environment as a grid with occupancy
values between 0 and 1, which is very simple. The beauty of occupancy grids is
that they can be derived from simply projecting arbitrary spatial information,
such as HD map data, object detection results, and even raw data from spatial
sensors like LIDAR or 4D Radar. Our research aims to find the optimal local
motion plan in complex and uncertain environments by directly applying the
spatial information integrated through such occupancy grids to nonlinear model
predictive control.
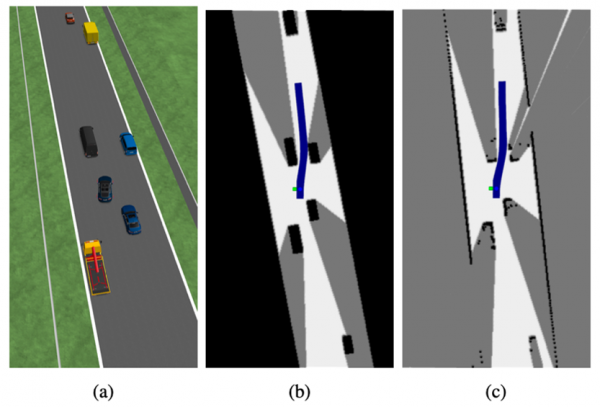
Fig. 1. Examples of
the obtained occupancy grid in real time in the same situation (a), utilizing
(b) object bounding boxes and road boundary information or (c) LIDAR point
clouds. The resulting trajectory plan by at that moment is shown along with the
bounding box of the ego vehicle.
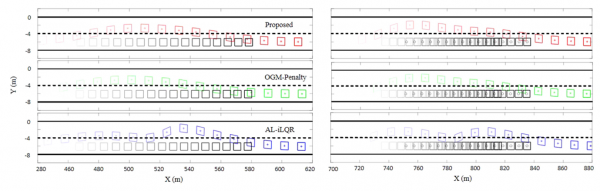
Fig. 2. Motion
planning tasks with moving objects.
<References>
Cho, Minsu, Yeongseok Lee,
and Kyung-Soo Kim. "Model Predictive Control of Autonomous Vehicles With
Integrated Barriers Using Occupancy Grid Maps." IEEE Robotics and
Automation Letters 8.4 (2023): 2006-2013.
GPU Hardware Accelerated Nonlinear Model Predictive Control
Collision
avoidance in emergency situations is a crucial and challenging task in motion
planning for autonomous vehicles. Especially in the field of optimization-based
planning using nonlinear model predictive control, many efforts to achieve
real-time performance are still ongoing. Among various approaches, the
iterative linear quadratic regulator (iLQR) is known as an efficient means of
nonlinear optimization. Additionally, parallel computing architectures, such as
GPUs, are more widely applied in autonomous vehicles. In this paper, we propose
1) a parallel computing framework for iLQR with input constraints considering
the characteristics of the problem and 2) a proper environmental formulation
that can be covered with single-precision floating-point computation of the
GPU. The GPU-accelerated framework was tested on a real-time
simulation-in-the-loop system using CarMaker and ROS at a 20 Hz sampling rate
on a low-performance mobile computer and was compared against the same
framework realized with a CPU.
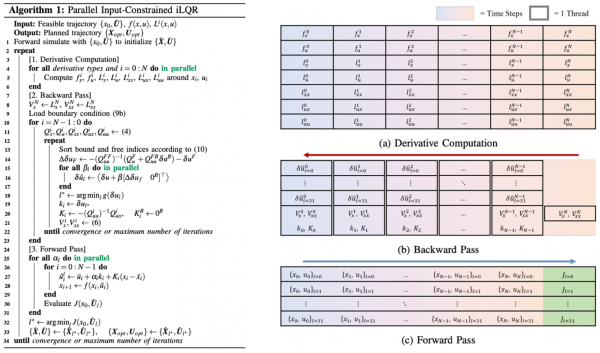
Fig. 3. Algorithm
details of GPU-Parallelized iLQR
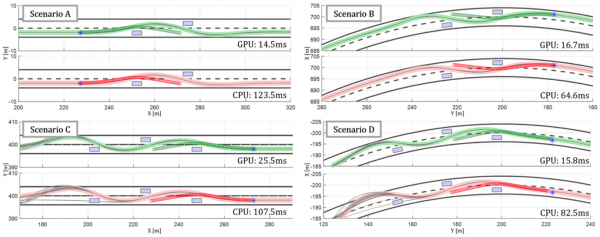
Fig. 4. Motion
results GPU vs CPU
<References>
Lee, Yeongseok, Minsu Cho,
and Kyung-Soo Kim. "Gpu-parallelized iterative lqr with input constraints
for fast collision avoidance of autonomous vehicles." 2022
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).
IEEE, 2022.